딥러닝의 정석 예제 코드 chapter 5 합성곱 신경망 CIFAR-10 학습
본 글은 딥러닝의 정석(Fundamentals of Deep Learning) chapter 5 합성곱 신경망
CIFAR 학습 예제 코드를 싣고 있다.
딥러닝의 정석의 예제 코드는
github에서 받을 수 있으나 몇몇 구문에서 오류가 발생하여 수정했다. 아마 python
버전이나, tensorflow 버전이 달라서 그런 것 같다.
CICFAR-10/100 데이터 세트는 Alex Krizhevsky, Vinod Nair 및 Geoffrey Hinton에 의해 수집되었으며, 각각
10/100개의 클래스를 가지고 해당 클래스의 훈련 및 테스트용 이미지를
제공한다. 아래 그림은 CIFAR 사이트에 있는 CIFAR-10의 예시이다
예제 코드에서는 CIFAR-10을
사용하였다. 아래 코드를 사용할 때 별도로 다운 받을 필요는 없다. 코드 실행 시
데이터가 없으면, 자동으로 다운받고 시작한다.
[소스 코드]
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import time, os,shutil
import cifar10_input
tf.reset_default_graph()
# Architecture
n_hidden_1 = 256
n_hidden_2 = 256
#parameters
learning_rate = 0.01
training_epochs = 1000
batch_size = 128
display_step = 1
def input(eval_data=True):
return cifar10_input.inputs(eval_data=eval_data,
batch_size=batch_size)
def distorted_inputs():
return cifar10_input.distorted_inputs(batch_size=batch_size)
def filter_summary(V, weight_shape):
#ix=weight_shape[0]
#iy=weight_shape[1]
#cx,cy = 8,8
V_T = tf.transpose(V,(3,0,1,2))
#tf.image_summary('filter',V_T,max_images=64)
tf.summary.image('filter',V_T,max_outputs=64)
def conv2d(input, weight_shape, bias_shape, visualize=False):
incoming = weight_shape[0]*weight_shape[1]*weight_shape[2]
weight_init =
tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=(2.0/incoming)**0.5)
W=tf.get_variable('W',weight_shape,initializer=weight_init)
if visualize:
filter_summary(W,weight_shape)
bias_init = tf.constant_initializer(value=0)
b = tf.get_variable('b',bias_shape,initializer=bias_init)
logit =
tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(input,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME'),b)
return tf.nn.relu(logit)
def max_pool(input, k=2):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input,
ksize=[1,k,k,1],strides=[1,k,k,1],padding='SAME')
def layer(input, weight_shape, bias_shape):
weight_init =
tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=(2.0/weight_shape[0])**0.5)
bias_init = tf.constant_initializer(value=0)
W = tf.get_variable('W',weight_shape,initializer=weight_init)
b = tf.get_variable('b',bias_shape,initializer=bias_init)
return tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(input,W)+b)
def inference(x, keep_prob):
with tf.variable_scope('conv_1'):
conv_1 =
conv2d(x,[5,5,3,64],[64],visualize=True)
pool_1 = max_pool(conv_1)
with tf.variable_scope('conv_2'):
conv_2 = conv2d(pool_1,[5,5,64,64],[64])
pool_2 = max_pool(conv_2)
with tf.variable_scope('fc_1'):
dim = 1
for d in pool_2.get_shape()[1:].as_list():
dim *= d
pool_2_flat = tf.reshape(pool_2,[-1,dim])
fc_1 = layer(pool_2_flat, [dim,384],[384])
fc_1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(fc_1,keep_prob)
with tf.variable_scope('fc_2'):
fc_2 = layer(fc_1_drop, [384,192],[192])
fc_2_drop = tf.nn.dropout(fc_2,keep_prob)
with tf.variable_scope('output'):
output = layer(fc_2_drop,[192,10],[10])
return output
def loss(output,y):
xentropy =
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=output,labels=tf.cast(y,
tf.int64))
loss = tf.reduce_mean(xentropy)
return loss
def training(cost, global_step):
tf.summary.scalar('cost',cost)
optimizer = tf.train.AdadeltaOptimizer(learning_rate)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(cost, global_step=global_step)
return train_op
def evaluate(output, y):
correct_prediction =
tf.equal(tf.cast(tf.argmax(output,1),dtype=tf.int32),y)
accuracy =
tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('validation error', (1.0 - accuracy))
return accuracy
if __name__ == '__main__':
if os.path.exists('conv_cifar_logs/'):
shutil.rmtree('conv_cifar_logs/',ignore_errors=True)
with tf.Graph().as_default():
with tf.variable_scope('cifar_conv_model'):
x =
tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,24,24,3])
y =
tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[None])
keep_prob =
tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
distorted_image, distorted_labels
= distorted_inputs()
val_images, val_labels = input()
output = inference(x, keep_prob)
cost = loss(output,y)
global_step =
tf.Variable(0,name='global_step',trainable=False)
train_op =
training(cost,global_step)
eval_op= evaluate(output,y)
summary_op =
tf.summary.merge_all()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sess = tf.Session()
summary_writer =
tf.summary.FileWriter('conv_cifar_logs/', graph_def=sess.graph_def)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
total_batch =
int(cifar10_input.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN/batch_size)
#Training Cycle
for epoch in
range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for i in
range(total_batch):
train_x, train_y = sess.run([distorted_image,distorted_labels])
_,
_cost = sess.run([train_op,cost],feed_dict={x:train_x,
y:train_y,keep_prob:0.5})
avg_cost +=_cost/total_batch
if epoch %
display_step == 0:
val_x,
val_y = sess.run([val_images,val_labels])
summary_str,accuracy = sess.run([summary_op,eval_op],feed_dict={x:val_x,
y:val_y, keep_prob:1})
print('epoch:',epoch+1,' cost:', avg_cost,' validation error:',(1-accuracy))
summary_writer.add_summary(summary_str,sess.run(global_step))
saver.save(sess,'conv_cifar_logs/model-checkpoint',global_step)
print ('optimization finished!')
val_x, val_y =
sess.run([val_images,val_labels])
accuracy =
sess.run(eval_op,feed_dict={x:val_x, y:val_y, keep_prob:1})
print('test accuracy:',accuracy)
[실행 결과]
training_epochs을 200인 상태의 결과다.
노트북이 너무 느리다.
epoch: 1 cost: 2.862300365399092 validation error: 0.90625
epoch: 2 cost: 2.4114405809304627 validation error: 0.875
epoch: 3 cost: 2.3529629456691232 validation error: 0.8984375
epoch: 4 cost: 2.3301569571861847 validation error: 0.8984375
epoch: 5 cost: 2.3214751958847053 validation error: 0.9140625
...
epoch: 198 cost: 1.581447203648396 validation error: 0.5
epoch: 199 cost: 1.579483058208075 validation error: 0.4765625
epoch: 200 cost: 1.5785948802263308 validation error: 0.46875
optimization finished!
test accuracy: 0.53125
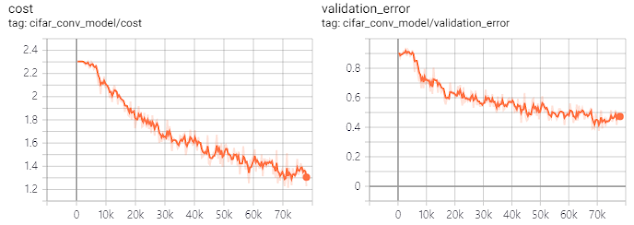
텐서보드로 본 loss/validation error 그래프는 아래 그림과 같다.
필터 이미지도 볼 수 있다.
관련 글:






댓글
댓글 쓰기